US Specified Risk Materials of Bovine Origin Materials Hague certification, consulate certification

In the field of food safety, when dealing with animal-derived products such as U.S. beef materials, special attention must be given to the management and certification of Specified Risk Material (SRM).
Below, we will discuss in detail the SRM regulations for U.S. beef materials, the Hague Apostille, and consular certification, as well as introduce the related agency services provided by the Washington, D.C. Notary Office.
What Are Specified Risk Materials (SRM) in U.S. Bovine-Origin Materials?
Specified Risk Materials (SRM) refer to parts of cattle that may carry the infectious agents responsible for Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), also known as mad cow disease. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), SRM includes, but is not limited to, the brain, eyes, and spinal cord of cattle aged 30 months or older. These parts are considered high-risk and must be specially handled or removed during food production and processing to prevent the spread of BSE.
In the global market, particularly in the European Union and Asia, strict regulations govern the management of SRM in imported beef. Therefore, beef products exported from the U.S. to these regions must comply with relevant safety regulations and undergo proper processing and certification to ensure product safety.
Case Study: Specified Risk Materials (SRM) in the U.S.
To be honest, this topic might sound complicated, but if we break it down into everyday terms, the logic becomes quite clear.
For example, if you’re dealing with Specified Risk Materials (SRM) of bovine origin in the U.S., the required documents are not as simple as a standard purchase contract or a basic commercial invoice. Instead, they must be endorsed by official and authoritative agencies.
In the U.S., the issuance and verification of documents related to SRM typically involve the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), along with relevant quarantine and health safety departments. This is because SRM plays a crucial role in international trade, particularly in the importation of raw materials for food, pharmaceuticals, and medical supplies. Strict regulations govern animal quarantine, food safety, and public health control.
These official U.S. documents are often issued in Washington, D.C., where major federal agencies, including the USDA headquarters, are located. Conducting these procedures in D.C. ensures that the process is standardized and properly regulated.
Why Is an SRM Document for U.S. Bovine-Origin Materials Needed?Let’s take a practical example: Suppose you run a company in China specializing in nutritional supplements or biopharmaceutical research and development. You want to import bovine-derived raw materials from the U.S., which have undergone strict quarantine and testing, to produce specialized products such as nutritional supplements, health products, or pharmaceutical intermediates for the Chinese market.
To do this, you must ensure that these materials have been legally inspected, meet quality standards, and comply with regulations in their country of origin. The U.S. issues official certification documents precisely to assure importing countries (such as China) that the bovine-derived materials are traceable, free from disease risks, and of certified quality.
On the Chinese side, a Specified Risk Material (SRM) certification issued in the U.S. is often processed in major cities such as Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou, where import-export trade is most active. This document is essential for customs clearance, inspection, record filing, and compliance with domestic regulatory requirements.
Having a certified U.S. document makes it much easier to navigate the subsequent processes in China. For instance, when customs officers, regulatory authorities, or industry supervisors review your paperwork, an officially endorsed U.S. certificate—especially one with an Apostille certification—immediately verifies its authenticity and credibility. This minimizes unnecessary verification steps, helping you expedite customs clearance, ensure regulatory approval, and move your products into production and sales more smoothly.
Why Is the “Washington, D.C. Notary Office” Mentioned, and Why Apply for an Apostille?The reason for mentioning the “Washington, D.C. Notary Office” (which actually refers to agencies or intermediaries handling notarization and Apostille applications in Washington, D.C.) is directly related to recent changes in international regulations.
On March 8, 2023, China officially joined the Convention Abolishing the Requirement of Legalization for Foreign Public Documents (commonly known as the Hague Apostille Convention), which took effect on November 7, 2023.
This change means that China no longer requires the previous cumbersome “dual authentication” process (first certification by the U.S. Secretary of State, followed by legalization at a Chinese embassy or consulate). Instead, China now directly accepts Apostille certification issued in the U.S.
As a result, when you authorize a notary office or certification agency in Washington, D.C. to apply for Apostille certification for a Specified Risk Material (SRM) document related to U.S. bovine materials, you are essentially ensuring its official recognition in China in a single step.
For clients, this eliminates the need to visit embassies or consulates for additional stamps, avoids back-and-forth processing between the U.S. and China, saves money, reduces wait times, and simplifies the entire process.
Once an official SRM document related to U.S. bovine materials is issued in Washington, D.C., it can be notarized and Apostille-certified locally. After that, it can be legally used in China without additional embassy or consulate legalization.
This streamlined process frees clients from complicated procedures, ensuring that documents are authoritative, legally recognized, and internationally accepted. It also simplifies the import process, reduces time and costs, and prevents unnecessary complications or misunderstandings—which is exactly what clients need.
We share case studies to help illustrate the process and practical applications.
Important Notice
All company names and personal identities mentioned in this document are fictional. Any resemblance to real entities or individuals is purely coincidental. These case studies are provided for reference only to offer a framework for understanding and decision-making.
When applying this information to your situation, please carefully assess your specific needs and seek professional advice or further verification if necessary.
What Is U.S. Apostille Certification?
Apostille certification, also known as Hague Apostille, is an international authentication method that verifies the legal validity of documents for use in countries that are members of the Hague Convention.
For documents related to bovine materials (such as health certificates, export certificates, and other official documents), an Apostille ensures that the document is recognized by the destination country without requiring further legalization.
In the U.S., Apostille certification is typically handled by the Secretary of State in each state. The process involves attaching an Apostille seal or label to confirm that the document was issued by a legally authorized person or agency.
What Is U.S. Consular Authentication?
Unlike Apostille certification, consular authentication is another method of document legalization, used for countries that are not members of the Hague Convention. This process ensures that a document is legally valid in another country.
Consular authentication typically involves multiple steps: after being certified at the state level, the document must also go through the U.S. Department of State and then be further authenticated by the consulate of the destination country.
For example, if a U.S. exporter wants to ship beef to a country that has not signed the Hague Convention, they must use this method to authenticate export documents to meet the import requirements of the destination country.
Washington, D.C. Notary Office Agency Services
Given that the document authentication process can be complex and time-consuming, the Washington, D.C. Notary Office offers comprehensive agency services to help businesses and individuals simplify the certification process.
Whether Apostille certification or consular authentication is required, the Washington, D.C. Notary Office provides professional assistance, including document preparation, submission of authentication applications, and tracking the certification progress.
By utilizing these specialized services, businesses can ensure their documents meet international legal requirements, enabling seamless international trade. This is especially crucial for sensitive exports such as beef, ensuring compliance with target market regulations and facilitating smooth business operations.
Apostille Sample
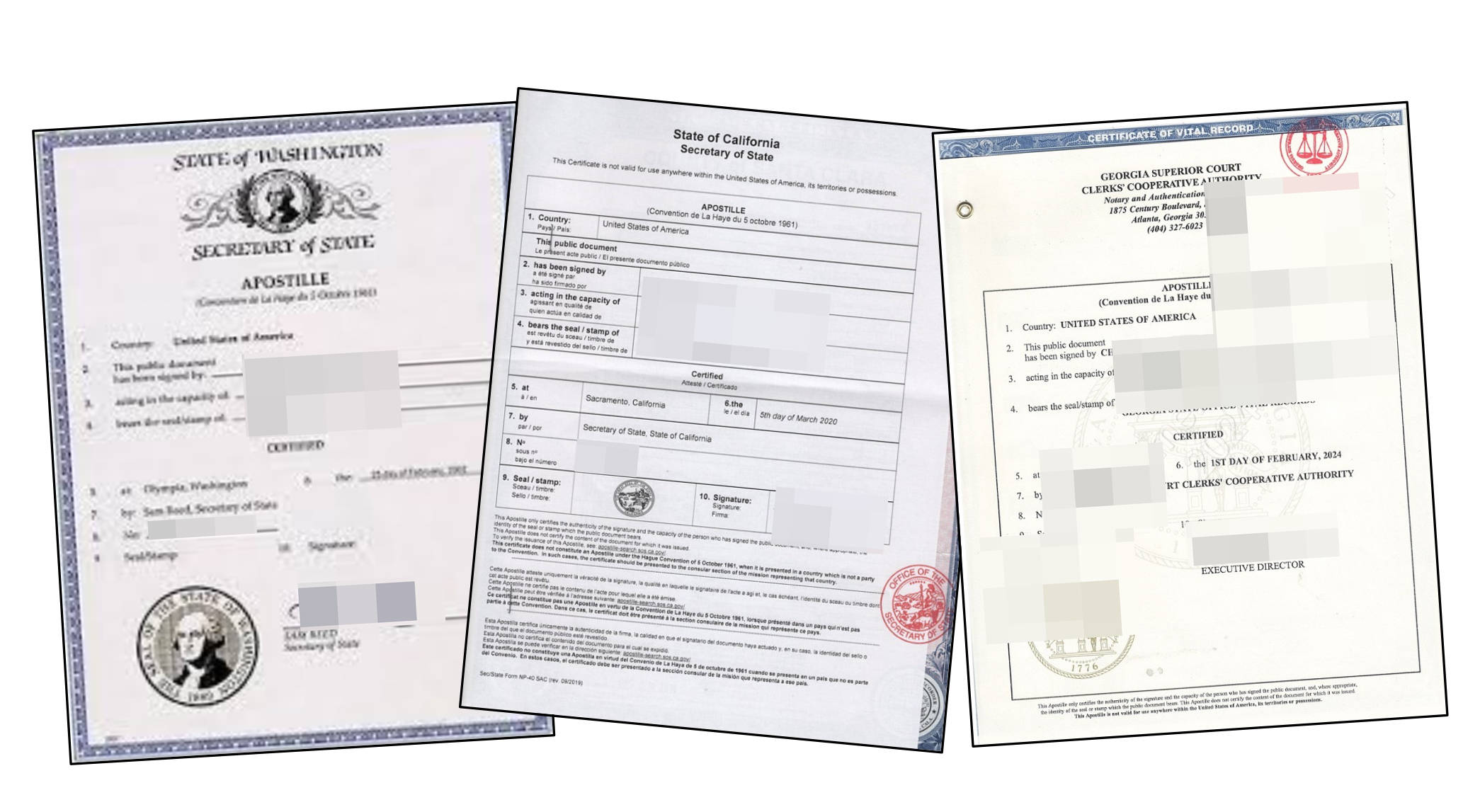
Authentication Sample
