Hague Certification and Consulate Authentication for U.S. Non-Clinical Research Special Certificate
- What Is the U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate?
- Case Study: U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate
- What Is the U.S. Hague Certification (Apostille)?
- What Is U.S. Consular Authentication (Authentication)?
- Washington, D.C. Notary Office Provides Authentication Services
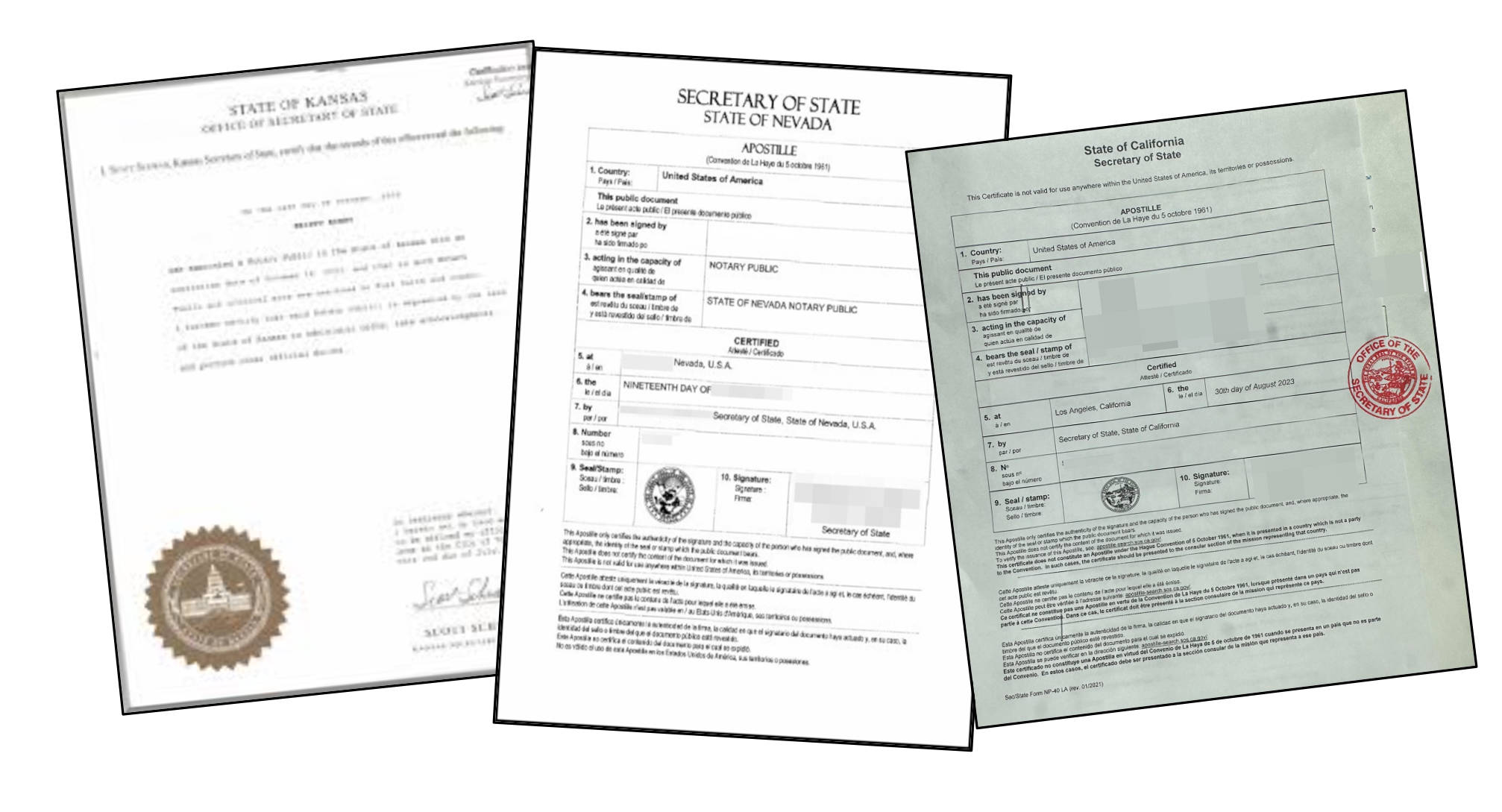
- Apostille Sample
- Authentication Sample

In the context of scientific research and technological development, the international certification of various certificates and documents is becoming increasingly important. Specifically, equipment, reagents, and software used in non-clinical research require specialized certificates to ensure their legal and safe use for research purposes. The U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate, along with the necessary Hague Certification and Consulate Authentication, plays a crucial role in international research collaboration and product exchange.
This article will provide a detailed overview of these certificates and authentication processes and explore how to obtain these services through the Washington, D.C. Notary Office.
What Is the U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate?
The Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate is a document specifically used to designate certain products—such as laboratory reagents, instruments, and software—as intended solely for non-clinical research purposes. This certificate indicates that the certified product is not approved for clinical testing or patient treatment.
The primary purpose of this certification is to ensure the legal use of these products within research environments. Since products with this certification do not go through the same regulatory review process as clinical-use products, they must be strictly used within the limits of research purposes.
Case Study: U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate
When it comes to the Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate in the U.S., it’s not something that can be easily obtained from just any institution. Typically, this type of certificate is issued by a state-level regulatory agency responsible for overseeing research permits or by an organization specializing in public affairs certification. For example, such a certificate might be granted by a relevant department under the jurisdiction of Washington, D.C., or by an institution that handles official document authentication.
Why is this certificate necessary in the U.S.? Let’s look at an example:
Suppose a Chinese pharmaceutical research company needs to acquire certain biological samples or reagents from the U.S. for non-clinical research. These materials often require local regulatory approval in the U.S.—which is where the Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate comes in. With this certificate, the company can legally conduct its research in China, ensuring that its experiments and research processes comply with both legal requirements and international standards.
Simply obtaining the Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate from the U.S. isn’t enough to make it legally usable in China. In the past, using U.S.-issued documents in China required consular or diplomatic authentication, which involved complex procedures, multiple steps, and running between different government offices for notarization and legalization. Each country had its own requirements, and preparing Chinese translations and notarized documents made the process even more complicated.
However, since November 7, 2023, when China officially joined the Convention Abolishing the Requirement of Legalization for Foreign Public Documents (commonly known as the Apostille Convention), things have become much simpler. Now, the Hague Apostille (Apostille) process allows a U.S.-issued Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate to be directly recognized in China, eliminating the need for consular authentication.
Here’s how it works:The client authorizes the Washington, D.C. Notary Office to apply for an Apostille for the certificate. This step is crucial because Washington, D.C. is the political center of the U.S., where government agencies are concentrated, making notarization and authentication more authoritative and efficient.
Once the client receives the U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate with an Apostille, using it in China becomes much smoother. For example, if a biopharmaceutical company in Shanghai or Beijing is conducting an international collaboration project, they may need this certificate to verify that the research materials or technology obtained from the U.S. are legitimate and recognized. With the Apostille, they no longer have to worry about China’s previously complex authentication procedures.
Since the Apostille Convention has taken effect, Chinese authorities at all levels now recognize foreign documents with an Apostille without requiring additional dual authentication or consular legalization.
From the client’s perspective, this process solves several key issues:
- Simplified authentication process – Previously, companies had to go through consulates and foreign affairs offices for multiple approvals. Now, an Apostille is enough.
- More control over time and costs – With fewer steps involved, waiting times are reduced, and service fees are lower.
- Guaranteed legal validity – A document certified with an Apostille is officially recognized in China, ensuring that the paperwork is legally valid and can be used without obstacles.
Suppose you are the head of a biotechnology company in China, and you order a batch of specialized reagents from a U.S. laboratory that are only for non-clinical research. Before using them in your lab for testing and validation, you need to prove that these reagents are compliant and that your research is legally authorized. It’s essential to ensure that the certification documents from the U.S. are recognized in China.
By authorizing a notary office in Washington, D.C. to process the Hague Apostille for the Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate, you can avoid unnecessary steps. Once the U.S. certificate is stamped with an Apostille, it is directly valid in China—allowing for a smooth and hassle-free international research collaboration.
This process not only makes cross-border cooperation more efficient but also gives confidence to both research teams and regulatory authorities.
Important Disclaimer
We share case studies to help illustrate the process and practical applications. Please note:
- All company names and personal names mentioned in this explanation are purely fictional. Any resemblance to real companies or individuals is purely coincidental.
- These case studies are for reference only, providing a framework for understanding and decision-making.
- Before applying this information to your situation, carefully evaluate your specific needs and seek professional advice or further verification if necessary.
What Is the U.S. Hague Certification (Apostille)?
The Hague Certification, also known as an Apostille, is an international authentication method used for official documents exchanged between member countries of the Hague Convention. This certification verifies the authenticity of signatures and seals on a document, ensuring that it is legally recognized in all countries that have signed the convention.
In the U.S., if a Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate needs to be used in another Hague Convention member country, it typically requires an Apostille to confirm its validity and authenticity.
What Is U.S. Consular Authentication (Authentication)?
When a U.S.-issued document needs to be used in a country that has not signed the Hague Convention, Consular Authentication (also known as Authentication) becomes necessary.
Similar to an Apostille, Consular Authentication verifies the authenticity of the signatures and seals on a document. However, instead of being processed under the Hague Convention, this authentication goes through both the U.S. Department of State and the consulate of the destination country.
This ensures that a U.S. Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificate can be widely accepted and recognized in countries that do not accept Hague Apostilles.
Washington, D.C. Notary Office Provides Authentication Services
For individuals or organizations needing Hague Apostille or Consular Authentication, the Washington, D.C. Notary Office offers comprehensive authentication services. This office not only helps clients understand the certification process but also reduces administrative burdens, ensuring that all necessary documents are officially authenticated according to international standards.
By utilizing the professional services of the Washington, D.C. Notary Office, clients can ensure that their Non-Clinical Research Use Only Certificates are seamlessly accepted and recognized by international partners.
Understanding the specific requirements and procedures for these certificates and authentications enables research institutions and companies to efficiently expand the legal use and exchange of their research products and services worldwide.
Apostille Sample
Authentication Sample
